代码分析基于Go1.13.4版本,不同版本间可能略有不同,但处理流程是一致的。
基本使用
Go内置了HTTP服务器,用户可以很方便的开发HTTP服务。一个简单的例子如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
package main
import "net/http"
type index struct {}
func ( index ) ServeHTTP ( w http . ResponseWriter , r * http . Request ) {
w . Write ([] byte ( "Index" ))
}
func main () {
http . Handle ( "/" , index {})
http . HandleFunc ( "/greet" , func ( w http . ResponseWriter , r * http . Request ) {
w . Write ([] byte ( "Great!!!" ))
})
if err := http . ListenAndServe ( ":3000" , nil ); err != nil {
panic ( err )
}
}
基本类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
type Handler interface {
ServeHTTP ( w http . ResponseWriter , r * http . Request )
}
type HandlerFunc func ( http . ResponseWriter , * http . Request )
// ServeHTTP calls f(w, r).
func ( f HandlerFunc ) ServeHTTP ( w ResponseWriter , r * Request ) {
f ( w , r )
}
这是HTTP库中最基本,最重要的一个接口了,接收一个Request,一个ResponseWriter.
额外的HandlerFunc是go中常用的一种模式,通常情况下,要想实现一个接口,需要定义额外的类型,不过可以通过定义一个对应的Func类型,Func类型实现该接口,只要函数签名一致,用户只需要定义对应的函数即可实现该接口,大幅度的简化了代码。
1
2
3
4
5
type ResponseWriter interface {
Header () http . Header
Write ([] byte ) ( int , error )
WriteHeader ( statusCode int )
}
路由
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
type muxEntry struct {
h Handler
pattern string
}
type ServeMux struct {
mu sync . RWMutex
m map [ string ] muxEntry
es [] muxEntry // slice of entries sorted from longest to shortest.
hosts bool // whether any patterns contain hostnames
}
func ( mux * ServeMux ) Handler ( r * http . Request ) ( h http . Handler , pattern string )
func ( mux * ServeMux ) Handle ( pattern string , handler Handler )
func ( mux * ServeMux ) HandleFunc ( pattern string , handler func ( http . ResponseWriter , * http . Request ))
func ( mux * ServeMux ) ServeHTTP ( w ResponseWriter , r * Request )
ServeMux保存了所有path到handler的映射,Handler方法提供了从Request中获取Handler的功能,Handle注册Handler到ServeMux中,HandleFunc注册HandlerFn到ServeMux中,实现ServeHTTP接口使得ServeMux可以作为Handler传入到另外一个ServeMux中,提供了多级路由嵌套的功能。
Server如何启动
http.ListenAndServe(TLS)
通过Addr和Handler初始化http.Server, 然后调用server的ListenAndServe方法
http.Server.ListenAndServe(TLS)
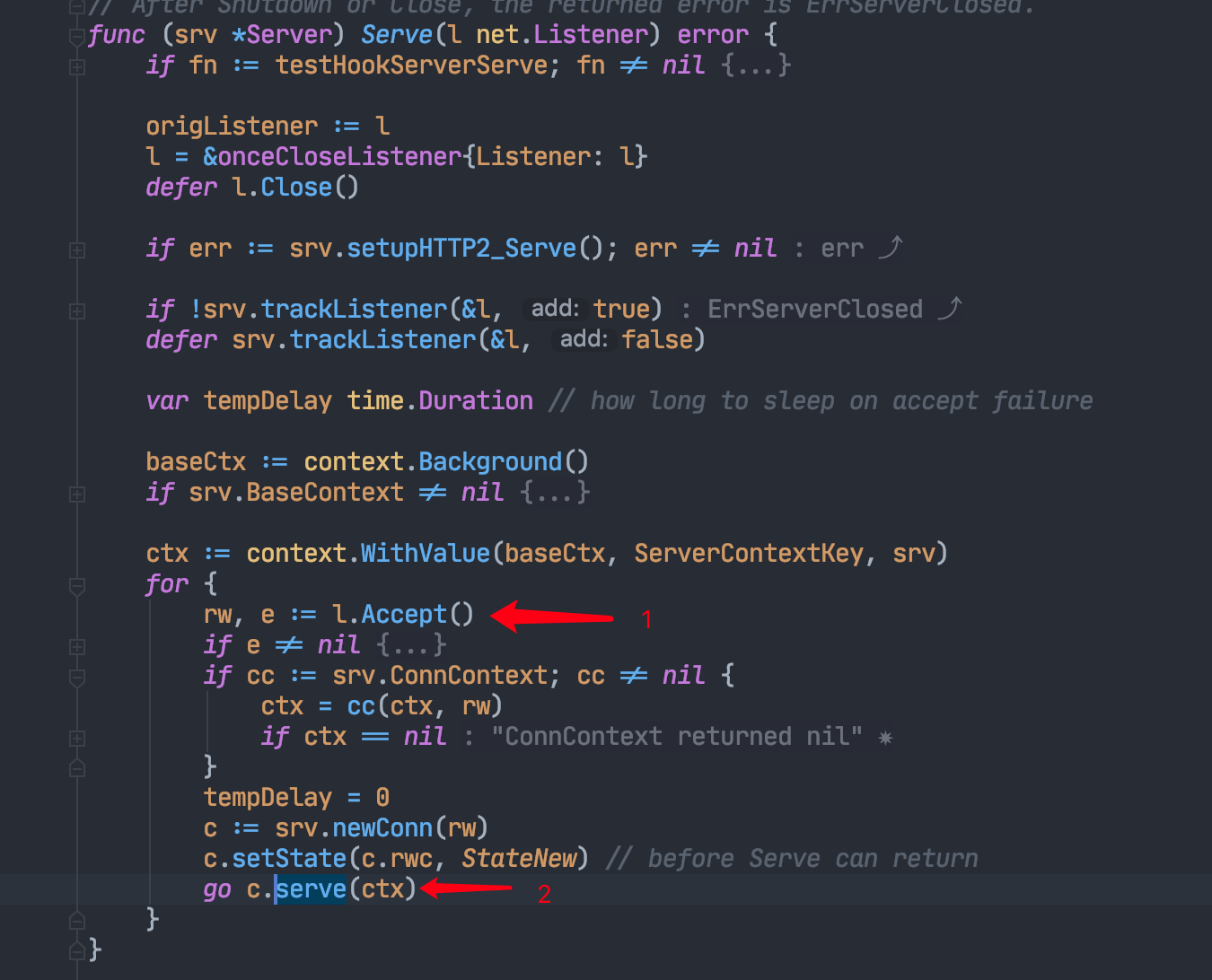
监听tcp端口
死循环监听新的连接,开启新的协程处理
go-std-http-server-serve.png
http.conn.serve
判断是否为TLS连接并握手,否则直接进行第二步。
循环读取Request并处理,见第三步。
根据Request的path从ServeMux中选择Handler处理。
go-std-http-conn-serve.png
内置的Handler类型
为了简化用户的开发,HTTP库中内置了一些Handler类型,下面一一解析:
http.FileServer
提供静态资源服务器,短短数行便可提供一个文件服务器,如下,将本地public路径映射到请求的/static路径
1
http . Handle ( "/static" , http . FileServer ( http . Dir ( "public" )))
http.NotFoundHandler
路径找不到时,会调用该中间件。
1
http . Handle ( "/404" , http . NotFoundHandler ())
http.RedirectHandler
客户端重定向。
1
http . Handle ( "/301" , http . RedirectHandler ( "/" , 301 ))
http.StripPrefix
在将请求定向到你通过参数指定的请求处理器之前,将特定的prefix从URL中过滤出去
1
http . Handle ( "/tmpfiles/" , http . StripPrefix ( "/tmpfiles/" , http . FileServer ( http . Dir ( "/tmp" ))))
http.TimeoutHandler
提供一个带有超时时间的Handler
1
http . Handle ( "/timeout" , http . TimeoutHandler ( http . HandlerFunc ( handler ), 1 * time . Second , "Timeout" ))
中间件开发
得益于良好的API设计,开发一个中间件是非常方便的。一个可能的中间件接口如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
type Middleware interface {
Call ( h http . Handler ) http . Handler
}
type MiddlewareFunc func ( http . Handler ) http . Handler
func ( f MiddlewareFunc ) Call ( h http . Handler ) http . Handler {
return f ( h )
}
标准库中的func StripPrefix(prefix string, h Handler) Handler便可作为一个中间件。
内置工具方法
HTTP库内置了大量的工具方法,这里选出常用的一些进行解析
http.Error
根据用户指定的错误码进行返回
http.NotFound
同上面的http.NotFoundHandler, 用户直接调用并返回
http.Redirect
同上面的http.RedirectHandler, 用户直接调用并返回
1
http . Redirect ( w , r , "https://localhost:9000/some/url" , 301 )
http.ServeContent
提供了用户下载的功能,支持断点续传
1
http . ServeContent ( w , r , "file.dat" , fileLastModTime , fileSeekReader )
http.ServeFile
同http.ServeContent,不支持断点续传
1
http . ServeFile ( w , r , fileName )
http.SetCookie
设置Response的Cookie
1
http . SetCookie ( w , cookiePtr )